City Scene with Nuns (1947) by Robert W. Addison, in the collection of the Art Institute of Chicago.
A long, hot summer is beginning to come to and end here in Chicago, and we have lots of great new images to share with you today. We thank all the original photographers, and our contributors.
We have many recent photo finds of our own, some great new ones thanks to Bill Shapotkin, and another batch that, for one reason or another, we were unable to purchase (but are still worth looking at).
We have been hard at work on our next book, Chicago’s Lost “L”s, and recently turned in all the text and images to our publisher. I am sure there will be additional changes (there always are), but I thought it would be useful to talk a bit about the process of making a book (see below).
We all have our ways of coping with situations. Working on a book has helped me keep focused during this pandemic.
Have a safe Labor Day weekend, everyone.
-David Sadowski
How a Book is Made

Technology may have changed since the 1950s, but you still have to go through your images one at a time.
My new book Chicago’s Lost “L”s is the third part of a trilogy, along with Chicago Trolleys and Building Chicago’s Subways. I got the idea for all three books some years ago, and have been collecting images with this in mind for nearly six years.
Without an idea, there is no book. While there have been plenty of books about Chicago’s famed “L”, each one is different. The subject is so large, an author has to put their own unique “spin” on it. I decided my brief would be to showcase those aspects of the “L” that don’t exist any longer.
This, I believe, many people are interested in. Whenever the subject of various “L” lines that no longer exist comes up, I get the feeling people want to know more about this. So there is a need.
You make a proposal to your publisher, and if they like what they here, you enter into a contract that has specifics of what they need, and deadlines for when you give it to them. Books to be don’t come with instruction manuals of how to put them together, though.
There, you’re on your own, and I am sure the creative process is different for every author, and for every book.
I realized the project was doable when I had collected most of the images I would need. The first thing I did was to go through my entire image collection and look at everything. I started setting aside any images that I thought could be relevant, using an image editor. I went through 20,000 images, and I did this three times– at the beginning, middle, and near the end of the project. That was necessary, because each time I was looking for something different.
One of the most important things and author needs to determine is, how will things be organized? Chronologically, geographically, or thematically? Each approach has advantages and disadvantages, and the subject usually needs a combination of all these.
Once I decided on what the chapters in the book would be, I started a folder in my image editor for each one. Then, I started sorting the images in each folder in order, shuffling and reshuffling them until I was happy with the results.
Even after I had selected the proper number of images, I eventually ended up replacing about one-third of them. As time went on, my book’s narrative began to develop. As it did, some images fit, and others did not.
After I was satisfied with my image choices, I began writing the captions to go with them. If I couldn’t figure out a good caption for something, it had to go. Everything that stays in the book needs a good reason for being there. Writing means rewriting, over and over, as many times as necessary to say what you want to say in the most economic and efficient way possible.
Along the way, you find that no matter how much research you have done, the book needs more. You figure out what’s missing, and you do everything you can to find those things that can complete the story you are trying to tell. In general, it’s the oldest things that are hardest to find.
As you learn more while putting things together, the book tells you what it needs to be, and this is always going to be somewhat different than what you thought it was at the start. You always need to dig deeper.
The last thing I wrote was the introduction. That’s the opposite of how I approached my previous two books, but this time I wanted to see what would be included in the book first.
I also spent many, many long hours working over images in Photoshop. This includes the various maps I am using. I want everything to look its best when you open up your copy of Chicago’s Lost “L”s and start reading it.
One thing I noticed, when sorting through my images, is how sometimes, when I had duplicates of an image, they weren’t always identical. It occurs to me that when black-and-white prints were made from medium-format negatives, they were probably made in batches, and the same neg could have been printed multiple times over the years. Each time, the neg would be positioned a bit differently.
Now it is possible to combine those images using a program called Microsoft Image Composite Editor. The result is an image that is closer to the full size of the negative. I was able to do this for five or six images in the book.
More information about Chicago’s Lost “L”s will follow, as available. Once a book is published, it belongs to the readers, and you can decide whether or not it is worthwhile, but whatever the result, I have given this project 110%.
When you challenge yourself to reach a goal, it forces you to do better. I learn so much every time I work on a new book– new skills, new methods, more efficiency, more organization, more knowledge. And when someone reads one of my books, and appreciates it (if they do), that’s the icing on the cake.

Howard Terminal looking west in 1959. Ultimately, this picture did not make it into the book.

The same location on June 6, 2020.

I spent a lot of time cleaning up this image, but decided not to use it. The steam engines Chicago used on the “L” were similar to those in New York, but they weren’t identical– they were more robust. They didn’t have the same specs.

I took this picture of the former Linen Avenue station in Wilmette on June 6, 2020, but it didn’t make the cut.

I spent considerable time cleaning up this track map of the Kenwood “L” before I found something else I chose to use.

The same goes for this map of the Stock Yards branch.

In this case, after putting the two versions of this image together, only a small amount was missing at the top, not difficult to replace.

You can see how the same negative was lined up slightly differently both times it was printed. It was not difficult to fill in the missing parts on the two corners and bottom.
Recent Finds

El Tracks (1949) by Robert W. Addison. The El looks like New York, but the streetcar seems more like Chicago.

The Chicago Aurora & Elgin owned everything west of Laramie Avenue, and in June 1953, were storing cars mid-day at Lockwood Yard (5300 W.). Wood cars 28 and 207 are seen, among others. (Ray Mueller Photo)

Mark Jesperson, who now lives in France, has written a Wilmette history article and is using one of our images. In turn, he sent us this nice picture, taken in the early 1950s at Linden Avenue, showing a gate car. Evanston became a shuttle to Howard starting in August 1949 (except for the Evanston Express).

An early Loop photo looking north from Tower 12 at Wabash and Van Buren. I think this is pre-1913, meaning it’s the left-hand-running bi-directional Loop. The Met car at left is going away from us on the Inner Loop, while that is probably a South Side car coming towards us, heading south.

Another early view of the Loop, again at Wabash and Van Buren, this time looking west.

When the Indiana Railroad interurban shut down in 1941, Lehigh Valley Transit bought high-speed car 55. Here, it’s on a Pennsylvania Railroad flatcar. LVT turned it into car 1030, showcase of their fleet on the Liberty Bell Route between Allentown and Philadelphia. It is now at the Seashore Trolley Museum. (H. P. Sell Photo)

CTA PCC 7363 at Devon Station (car barn), possibly in 1957. Part of the building here was destroyed by fire years earlier.

LVT high-speed 1022. Except for 1030, all the modern lightweight high-speed cars on the Liberty Bell Limited were ex-Cincinnati & Lake Erie.

LVT 1008 in Allentown.

Cook County #1 was used to transport mental health patients between facilities such as Dunning on Chicago’s northwest side. Don’s Rail Photos: “1, hospital car, was built by CSL in 1918. It was retired on September 21, 1939.”

June 21, 1958 was the day before the new Congress-Douglas-Milwaukee line went into regular service. It was also the last day the Douglas Park trains ran downtown over the Lake Street “L” . Photographer Bob Selle was riding a northbound Douglas train when he took this picture, showing the station at Madison and Paulina, which had not been used in over seven years.

CTA wood car 1712 is a Kenwood shuttle train at the Indiana Avenue stub terminal, probably circa 1953. It was built by St. Louis Car Company in 1903 for the Northwestern Elevated Railroad. (Robert Selle Photo)

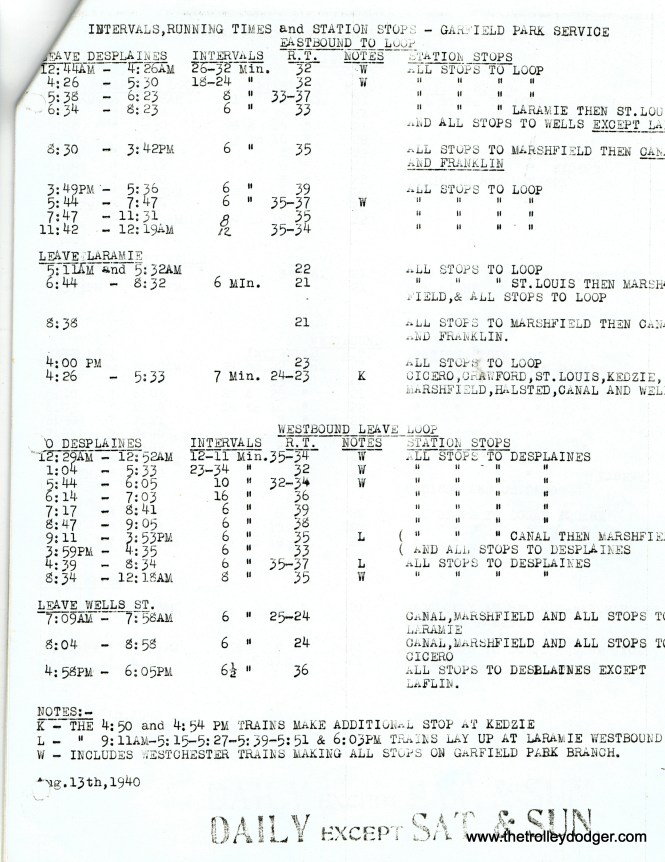
A night shot of CTA 4219 at Laramie Avenue on the Garfield Park “L” on January 4, 1957. (Robert Selle Photo)

A night shot of CTA 4434 at Laramie Avenue on the Garfield Park “L” on January 4,1957. (Robert Selle Photo)

CTA 2840, a Met car, at Laramie Yard on January 4, 1957. (Robert Selle Photo)

A night shot of CTA 2810 and 2818 in the Laramie Yards on February 1, 1957. By then, the Congress Expressway was open as far as Laramie and was adjacent to the Garfield Park “L”. It was still under construction west of here, and the “L” ran on temporary trackage. (Robert Selle Photo)

CTA 2802 at Laramie Yard (Garfield Park “L”) on February 1, 1957. (Robert Selle Photo)

The CTA temporarily stored many wood cars at Laramie Yard after they were retired and awaiting scrapping. Here, we see 1752, among others, on November 24, 1957. I assume these cars were last used on Evanston and Ravenswood. (Robert Selle Photo)

CTA 1782 and 1785 at Laramie Yard on November 24, 1957. As far as I know, scrapping took place at Skokie Shops. (Robert Selle Photo)

CTA 3119, signed as a Lake Street local, is being stored on the third track at Hamlin in August 1948. By then, A/B “skip stop” service had been in effect for some months. It’s possible this car was no longer being used on the line. Don’s Rail Photos: “3119 was built by St. Louis Car in 1902 as LSERR 119. In 1913 it was renumbered 3119 and became CRT 3119 in 1923.”

CTA Met car 2113 at Laramie Yard in August 1948. Don’s Rail Photos: “2104 thru 2154 were built by Pullman in 1894 as M-WSER 104 thru 154. In 1913 they were renumbered 2104 thru 2154, and in 1923 they became CRT 2104 thru 2154.” This would have been one of the original cars used on the Metropolitan West Side Elevated when it opened in 1895.

Chicago Rapid Transit Company medical car 2756 at Laramie Yards on September 19, 1934. It was built by Barney & Smith in 1895 and had been used as a funeral car. It could carry baggage as well as passengers.

Chicago & West Towns 158 at Brookfield Zoo in the summer of 1939. This is the south entrance. The Zoo opened in 1934 and was just north of the C&WT line to LaGrange, which cut through the Forest Preserves on private right of way.

The back end of the West Towns car barn in Oak Park. The street sign identifies this as North Boulvard and Cuyler. This is undated but could be 1939. The Chicago & North Western embankment is just to the right out of view. After being used for buses into the 1980s, this building was demolished and replaced by a Dominick’s Finer Foods store. After that chain went out of business, that building was remodeled into Pete’s Fresh Market. We are looking to the northeast.

C&WT line car 15, probably at the car barn at Harlem and 22nd Street (Cermak), in North Riverside. On pictures, this was often mistakenly identified as Berwyn, but that’s across Harlem Avenue just to the east.

Chicago Aurora & Elgin 406 makes a photo stop at State Road on the Batavia branch on August 8, 1954. The occasion was a Central Electric Railfans’ Association fantrip. (Robert Selle Photo)

A two-car Garfield Park “L” train, just west of Laramie Avenue in August 1948.

Caption: “Chicago El showing curve at Harrison and Wabash, taken from Congress Street station, April 2, 1939.” This curve has since been straightened out. The view looks south. (Duncan L. Bryant Photo)

A westbound Evanston Express train is on the Lake Street leg of the Loop near Clark. The view looks east. I assume this picture is from the 1940s, as the sign mentions Skokie instead of Niles Center. Miles Beitler: “There appears to be a propane bus in RBK275, visible just below the motorman’s cab on the Evanston Train. If so, it dates the photo to 1950 or later.” If so, why does the sign say Skokie, as the Niles Center route was converted to bus in 1948?

A Douglas Park “B” train heads west at (I think) Halsted on the Met main line, prior to the removal of two tracks for expressway construction.

The two CTA freight locos, S-104 and S-105, at Howard Street.

DesPlaines Avenue Yard in the 1960s, with a 2000, 6000s, and a couple of wood cars. The Met car looks like it has been converted to a snow plow, while the car on the right may have been used as an office or for storage.

Chicago Aurora and Elgin 405, circa 1950, scanned from the original negative. (Railway Negative Exchange) “Railway Negative Exchange (REX), also referred to as RNE was run by Warren Miller who lived in Moraga, CA. Born in Oakland, CA–(1923) Warren was this nation’s foremost authority on Western railroads and devoted virtually his entire life to assembling more than a quarter of a million negatives, most in glass plates, as well as over 200,000 photographs. Upon Warren’s death (1989), his collection was left to his nephew, Bob Hall. Bob has continued his uncle’s devotion to the railroad photographic hobby.” (2008)

CA&E 411 at the Wheaton Shops. (Railway Negative Exchange)

“CA&E Special #310 on the Mt. Carmel line, at the point where it switches off the main line from Chicago to Wheaton, IL (photo stop).” This was a Central Electric Railfans’ Association fantrip on August 8, 1954. (Robert Selle Photo)

CTA 398, D5, and 6148 at 70th and Ashland on June 28, 1952. (Robert Selle Photo)

“CTA car 649 on curve leading into south end of Limits barn (Clark and Schubert streets). 6148 at right (October 10, 1953).” (Robert Selle Photo)

CA&E 18 at Wheaton on August 15, 1952. Don’s Rail Photos: “18 was built by Niles Car in 1902. It was modernized in March 1941 and retired in 1955.”

“CTA “L” car lineup at DesPlaines Avenue yards, July 6, 1958.” (Robert Selle Photo)

“CTA “L” cars view at DesPlaines Avenue yards, July 6, 1958.” (Robert Selle Photo)

“CTA– one of the entrances to the Racine Avenue station on August 13, 1958.” (Robert Selle Photo)

CTA 4000s at Clark and Lake in January 1970.

Morning commuters on the Evanston Express in April 1970.

Wood cars at Randolph and Wabash in July 1957. At right, the Kodak Store (133 N. Wabash Avenue) and Blackhawk Restaurant (home of the spinning salad bowl) are visible.

Altman Camera, at 129 N. Wabash, was the Noah’s Ark of camera stores from 1964 to 1975. Owner Ralph Altman kept two of everything in stock– one to show, and one to go. This was literally the finest camera store in the United States. This was close to the location of the old Eastman Kodak Store, which I believe had to close in the mid-1950s due to anti-trust concerns. Here is Altman’s in 1967.

CTA 2519, among others, form a three-car train at Van Buren and Ogden. This must be in the early days of the temporary Garfield Park “L” operation, since the old “L” is still standing at left. The portion to Paulina (1700 W.) had to be kept until April 1954, as the Douglas Park “L” was still using it then. We are looking west at about 1800 W. Van Buren, and the “L” west of here was taken down pretty fast to facilitate expressway construction.

The same location today. The Eisenhower Expressway (formerly Congress) is behind those shrubs to the left.

The Congress median right-of-way on November 9, 1959. I believe we are looking east.

An Evanston Express train at Clark and Lake, possibly in the early 1970s.

CTA 1706 is signed for Stock Yards, but is obviously a Kenwood train at Indiana Avenue. Not sure if this is before or after Kenwood became a shuttle in 1949. I assume it simply has the wrong sign on it. It’s been suggested that in latter years, CTA may have through-routed Stock Yards and Kenwood trains. In actual practice, this wouldn’t have been easy, as it would have involved a lot of switching across the main line here.
Miles Beitler writes:
Great photos on your newest post!
Regarding photo RBK 511, on which I left a comment, I have attached information from my 1944 Rand McNally guidebook which describes CRT operations and indicates that, during non-rush periods, Kenwood trains did run from 42nd Place all the way to the Stock Yards. Apparently the CRT had a way to run the trains straight through the Indiana station. (I long ago sent scans of my guidebook to Graham Garfield, who posted them to his website.)
Your “Lost L’s” book sounds interesting and I intend to purchase it when it’s released.

Thanks. This was in the pre-CTA era. Once the Authority took over, there was a real push to reduce the amount of such switching maneuvers, adding and cutting cars in stations, etc. as these things are quite labor intensive.

CRT 2322 on February 12, 1939. It was built for the Met in 1901 by American Car and Foundry. (La Mar M. Kelley Photo)

CSL “Matchbox” 1352 signed for Taylor-Sedgwick-Sheffield. I wonder where this could be? Paul Wallace identifies this as 1044 N. Orleans Street.

The same location today.

CTA 1674 on Division by the north side “L” on June 25, 1950. This station had been closed on August 1, 1949 as part of the CTA’s major revision of north-south service. On the back of the print, it notes that these cars were “replaced by big Pullmans a few weeks later.”

Elevated train tracks on Van Buren Street, looking west from Franklin Street, 1914. That’s the Franklin and Van Buren station, used exclusively by the Metropolitan “L”.

An early track arrangement, showing the four-track Metropolitan main line on the east side of the Chicago River.

Figuring out which Loop tower this is took a bit of doing, but the Sterling Cycle Works was located on Wabash Avenue in 1897, making this Tower 12 at Wabash and Van Buren, looking east.

This circa 1897 ad shows Sterling Cycle Works on Wabash. However, this pre-dates the renumbering of Chicago streets, where the city shifted to a grid system, with numbers starting at State and Madison.
From the Collections of William Shapotkin

CTA 194 at Halsted and 64th in 1952.

The Lake Street “L” in 1962, looking east at Ridgeland. This must be just before the “L” was relocated to the Chicago & North Western embankment. M&C Motors, at right, was located at 315 South Boulevard.

Ridgeland and South Boulevard today.

The Lake Street “L” ramp between Central Avenue and Laramie circa 1961-62. This was after the changeover point between third rail and overhead wire was moved west of here. I think this picture was taken looking north on Latrobe.

The same location today.

CTA 4227 in the shop (Skokie?) in 1956.

CTA 3073 on route 52 (Kedzie).

South Side Rapid Transit car #1 in 1962. It is now at the Chicago History Museum.

CTA 279.

CTA 990 at 47th and Lake Park in March 1949. The Kenwood Hotel was located at 47th and Kenwood nearby.

CTA 940.

CTA 5315.

CTA 460 at 77th and Vincennes in March 1956, when it was part of the CTA Historical Collection. Looks like PCC 4021 is behind it. Both cars are now at the Illinois Railway Museum.

CTA 3093.

CTA 3095.

CTA 4244 on State Street in 1954.

CTA 129. M.E.: “This scene has to be at the western end of the main 63rd St. line, at Narragansett and 63rd Place. The tight loop shown in the picture was built when one-ended PCC cars started running on 63rd. This picture had to be taken in 1952 or 1953 after the pre-war PCC cars were removed from 63rd and assigned to Cottage Grove. The last cars to run on 63rd were the old red Pullmans like this one.”

A CTA 4000, most likely at a railway museum.

CTA 7213. (Robert W. Gibson Photo) M.E.: “You might add to the caption that this car was the last one to run in Chicago. Refer to all the pictures taken at 81st and Halsted and then on the final trip to the 77th and Vincennes barn in June 1958.”

CTA 7263 at Harrison and State in 1954.

Experimental forced-air ventilation on a CTA 6000. Not sure if you could open the windows on this car or not.

CTA 7023 at Clark and Van Buren on June 6, 1954.

Scrapped streetcars, including work car AA57, at South Shops. Don’s Rail Photos: “AA57, salt car, was built by St Louis Car Co in 1903 as CUTCo 4835. It was renumbered 1306 in 1913 and became CSL 1306 in 1914. It was rebuilt as salt car in January 1934 and renumbered AA57 on April 15, 1948. It was retired on December 14, 1956.”

CTA 6669 with experimental roof-mounted air conditioning, in storage on the middle track at Western Avenue on the Ravenswood. Just about every new feature CTA introduced on the 2000s was first tried out on 6000s.

CTA 6151, 3196, and 554 at 69th and Ashland. M.E.: “Route 45 was the Ashland-Archer-Clark route, similar to route 42, Halsted-Archer-Clark, but different in that route 45 always used old Pullmans whereas (at this time) route 42 used postwar PCCs.”

CTA 3179 at Grand and Navy Pier in March 1950.

CTA 7217 awaiting scrapping on June 30, 1959, at South Shops.

CTA 3231, 369, 988, and AA103 at 69th and Ashland in May 1949. M.E.: “The Green Hornet PCC in this picture would have been assigned to Western Ave. When the 69th/Ashland barn closed, but Western still operated PCC streetcars, those cars were moved to the 77th and Vincennes barn. To get there, they traveled east on 69th St. to Wentworth, south to 73rd, then southwest on Vincennes to 77th St.”

CTA 7113 at State and 62nd Place on November 9, 1955. This was where a PCC derailed and collided with a gasoline truck in 1950, a horrific crash that killed 34 people. M.E. “As I recall, the 1950 accident was not due to derailing, instead due to a misaligned switch on the southbound track which the motorman didn’t see but put his streetcar in the path of the northbound gas truck.” While that was the cause of the accident, since the PCC was going perhaps 35 mph at the time, it must have left the rails during the crash.

CTA 6413 at Skokie Shops on January 26, 1975. (Ronald J. Sullivan Photo)

CSL 5177 at Archer and Cicero in March 1935. M.E.: “The building behind the streetcar has a sign for United Airlines. So this scene is at Midway Airport, most likely north of 62nd St., which is where the Cicero car line ended in front of the original Midway terminal building. The sign on the streetcar reads Archer-Cicero, which was likely its northern destination.”

CSL 5519 at Archer and Rockwell in May 1943.

CSL 5130.

CSL 5083. M.E.: “The sign on the car appears to read Pitney-Archer. I went to Google maps, entered Pitney St. Chicago, and up came a map showing that Pitney starts at Archer and heads southeast from there. (All of this is about a block east of Ashland.) So maybe there was a carbarn at Pitney and Archer, or a stub on Pitney.”

CTA 914 in March 1950. The location is given as Archer and 38th Place.

CSL 775 at 47th and Indiana in May 1945.

CTA 7218, 4378, and 4399 at South Shops in August 1959, more than a year after the last Chicago streetcar ran.
More Ones That Got Away

Both Jeff Marinoff and I regret not winning this auction, which sold for $131.32. That’s a lot of money, but pictures of the Kinzie Street “L” station are rare indeed, It was located approximately where the Merchandise Mart station is now, and was open from 1900 to 1921, when it was replaced by a new station at Grand Avenue a few blocks north. Behind the “L”. to the left, is the Chicago and North Western station, which closed in 1910, so the view looks west.

Chicago & North Western station in 1881.

This, and the photos that follow, were offered as a batch of 11 original slides. I did bid on this but was not the top bidder, and they sold for about $100. That may seem like a lot, until you work out that it’s only about $9 per slide, and some of these are definitely keepers. All were taken between 1959 and 1963. Here are a pair of 6000s on the Congress line in Oak Park.

The old Lake Street Transfer station, closed since 1951. We are looking west. It was removed in 1964, along with that portion of the Paulina “L” north of here (excepting the bridge). I had originally said this was looking east. Graham Garfield: “We are looking west…” I believe we are actually looking east, from Wood St west of the station. The Met platforms began at Lake Street and projected northward (as seen in the attached Sanborn map), and in the photo they go to the left (which would be north, if we were facing east). Also, the building in the left foreground is still there today, located on the north side of Lake St near Wood St — here is a Google Street View of it from 2009 (I chose an older one because more recently it has been repainted and had its windows changed; you can still tell it’s the same building, but the older view makes it more obvious): https://goo.gl/maps/jb27nadEmRdf7BM16 “

CTA single-car unit 35 at Forest Park.

A two-car train of 4000s heads west on the Lake Street “L” when the outer portion still ran on the ground. I think the top of the building we see above the C&NW embankment is the Austin Town Hall, meaning we are between Laramie and Central circa 1961-62. The newspaper box at left is selling Chicago’s American, an afternoon newspaper. Tracks here may be using third rail as the conversion point to overhead wire was moved to Central Avenue while work was being done to put the line onto the embankment.

a westbound Lake Street “L” train in Oak Park. That stairway may be where one of the other pictures in this series was taken from. I assume this was located at the east end of the C&NW’s Oak Park station.

Looking east from Harlem Avenue in 1963. The Lake “L” is now on the embankment, but the old tracks and the Marion Street station are still in place. A train of CTA’s high-speed cars is in the station. The fans called them “circus wagons.”

The ground-level Lake Street “L’ in a somewhat underexposed shot. A “B” train heads east from the Marion Street station.

A westbound Lake “A” train at Home Avenue in Oak Park.

Looking north towards the Howard “L” station.

A two-car train of CTA 6000s on the turnaround loop in Forest Park, west end of the Congress-Milwaukee line. That loop-shaped thing on the front of the train was used for route selection, since these trains shared tracks with Douglas-Milwaukee trains further east of here.

An eastbound Lake Street “B” train heads east between Central and Laramie, and is about to head up the ramp to the “L” structure. This is just east of another picture in this series.

This is Waterloo, Cedar Falls & Northern car 100, shortly before it was destroyed by fire in 1967. I was surprised when this original slide sold for very little. Don’s Rail Photos: “100 was built by McGuire-Cummings in 1914. It was built as a second motor to operate behind the 140s as a two car train. The baggage compartment was a kitchen, and the rear end was an open platform observation. The buffet section was replaced with coach seats in 1918. The car was then rebuilt with a control station and baggage compartment in 1928 and the rear platform was enclosed at that time. It was the last interurban left on the WCF&N when it became diesel freight, and it was donated to the Iowa Chapter of the NRHS in 1956. It was moved to Centerville and operated on the Southern Iowa Ry. When the SI cut back its operation and dieselized, the Iowa Chapter transferred the car to the Iowa Terminal RR in 1966. Shortly after it was repainted and put into charter service, it was destroyed in the carbarn fire early November 24, 1967. It had been the only car saved from the WCF&N roundhouse fire on October 31, 1954, when the other two cars of its class burned.”

The Liberty Bell Limited in 1951 at Sellersville.

4000s at Linden Avenue in 1967.

Looks like a photo stop on the Illinois Terminal in 1956. Perhaps the final day for these lines?

2000s on the Lake Street “L” in 1965, looking west-southwest from the Chicago & North Western platform in Oak Park.

6000s cross the Chicago River in 1968. We are looking east.



The New York elevated, probably in the 1890s when steam was in use. Not sure which line this is.

The interior of Lehigh Valley Transit car 704 in 1951, used on the Liberty Bell interurban line in Philadelphia. The motorman would most likely punch a couple things in on that cash register and it would issue a ticket.

Somewhere in Evanston. Graham Garfield: “This is at Madison Street, a block or so south of Main station. Here is a view of the same location today, in a video of the line posted by CTA: https://youtu.be/tag-0WOzn7o?t=6303 (pretty soon after the video starts you’ll need to pause it to study the location) — the building on the right is the back of old Evanston Fire Station #2 (now the Firehouse Grill restaurant), and although the windows have been bricked over, the brickwork along the top of the wall facing the the track and the clay tiled parapet perpendicular to the tracks are identifiable. “

This is the State Street Subway in August 1965. I would have bid on this one if it had been sharper.

The Chicago, Lake Shore and South Bend, predecessor of the South Shore Line, in East Chicago, Indiana prior to 1926.

The Chicago, Lake Shore and South Bend, predecessor of the South Shore Line, in East Chicago, Indiana prior to 1926.

North Shore Line line car 604, photo by Gordon E. Lloyd at Highwood on June 13, 1959. Another original slide.

I couldn’t believe it when I saw that this original North Shore Line slide had sold for only $17.50. I expected it to go for a lot more and hence didn’t bid on it. It was taken by Gordon E. Lloyd on October 17, 1958 at Highwood.

A photo stop on the Hagerstown & Frederick interurban in Maryland.

Bill Shapotkin writes, “Both Andre Kristopans and I believe this is Main St. That said, he believes we are looking north (citing a curve in the distance). I am thinking we are looking south (lights to left are along Chicago Ave).” John McElroy: “I have lived in Evanston 60 years and rode the Evanston line all during this time. I believe the photo in question is taken at Davis Street, looking south, before the newer station was built here. The street visible is Benson Avenue, and the water tower is, I think, on the old building once occupied by Wieboldt’s. As you know, there is a curve south of Davis Street.” Graham Garfield adds, “this isn’t Main looking north, it’s Davis looking south. Both stations have curves to the left right after them in the directions cited, but here are some clues as to why this is Davis:
– The wooden “telephone” poles along both sides of the ROW have poles with no crossarms on the left and the ones with crossarms on the right. Photos of this part of the Evanston branch show that the crossarm poles were along the west side of the ROW, and the plain ones were along the east side of the ROW.
– The water tank visible in the left background shows up in lots of shots of Davis station looking south.
– They say the lights on the left under the platform are Chicago Ave, but if this was Main looking north Chicago Ave would be on the right, not the left. Also, Chicago Ave isn’t that close to the ROW at Main St; it’s about 60 feet from the ROW there. That’s Benson Ave on the left under the platform, which does run right alongside the ROW at Davis station.
– In this era, the station name signs varied in length, and were however long (or short) they needed to be to fit the station name on them. There is one visible on the left, right before the canopy, and while it is illegible we can see it is very long. While “Main” and “Davis” are short names, the ones at Main St just said the street name, but the ones at Davis were very long, reading, “Davis St – Downtown Evanston”.”

State and Van Buren in cable car days, between 1897 and 1906.

Congress looking west from Racine in 1967.

I think this one was undated, but I would guess maybe 1967 as 2000s are running on Douglas Park.

Looking south from Wilson Avenue in 1960.

Listed as Howard, this looks like Chinatown on the Dan Ryan line, circa 1970.

Could this be Isabella looking north?

Jeff Marinoff: “It shows car #122 of the Chicago Consolidated Traction Company. The roof destination sign reads Halstead & Irving Park Blvd.” CCT eventually became part of Chicago Railways Company. The photo dates to between 1900 and 1910.

This and the next picture show the aftermath of an “L” derailment at Wabash and Van Buren, which I assume took place on May 12, 1942. That’s Tower 12.

1939 Chicago Surface Lines Training Program

In 2016, we were fortunate to acquire a rare 16″ transcription disc, made in 1939 for the Chicago Surface Lines. This included an audio presentation called “Keeping Pace,” about 20 minutes long, that CSL used for employee training.
We were recently able to find someone who could play such a large disc, and now this program has been digitized and can be heard for the first time in more than 80 years. We have added it as a bonus feature to our Red Arrow Lines 1967 CD, available below and through our Online Store.


RAL
Red Arrow Lines 1967: Straffords and Bullets
# of Discs – 1
Price: $14.99
This disc features rare, long out-of-print audio recordings of two 1967 round trips on the Philadelphia & Western (aka “Red Arrow Lines”) interurban between Philadelphia and Norristown, the famous third rail High-Speed Line. One trip is by a Strafford car and the other by one of the beloved streamlined Bullets. The line, about 13 miles long and still in operation today under SEPTA, bears many similarities to another former interurban line, the Chicago Transit Authority‘s Yellow Line (aka the “Skokie Swift”). We have included two bonus features, audio of an entire ride along that five mile route, which was once part of the North Shore Line, and a 20-minute 1939 Chicago Surface Lines training program (“Keeping Pace”). This was digitized from a rare original 16″ transcription disc and now can be heard again for the first time in over 80 years.
Total time – 73:32

The Trolley Dodger On the Air
We appeared on WGN radio in Chicago in November 2018, discussing our book Building Chicago’s Subways on the Dave Plier Show. You can hear our 19-minute conversation here.
 Chicago, Illinois, December 17, 1938– Secretary Harold Ickes, left, and Mayor Edward J. Kelly turn the first spadeful of earth to start the new $40,000,000 subway project. Many thousands gathered to celebrate the starting of work on the subway.
Chicago, Illinois, December 17, 1938– Secretary Harold Ickes, left, and Mayor Edward J. Kelly turn the first spadeful of earth to start the new $40,000,000 subway project. Many thousands gathered to celebrate the starting of work on the subway.
Order Our New Book Building Chicago’s Subways

There were three subway anniversaries in 2018 in Chicago:
60 years since the West Side Subway opened (June 22, 1958)
75 years since the State Street Subway opened (October 17, 1943)
80 years since subway construction started (December 17, 1938)
To commemorate these anniversaries, we have written a new book, Building Chicago’s Subways.
While the elevated Chicago Loop is justly famous as a symbol of the city, the fascinating history of its subways is less well known. The City of Chicago broke ground on what would become the “Initial System of Subways” during the Great Depression and finished 20 years later. This gigantic construction project, a part of the New Deal, would overcome many obstacles while tunneling through Chicago’s soft blue clay, under congested downtown streets, and even beneath the mighty Chicago River. Chicago’s first rapid transit subway opened in 1943 after decades of wrangling over routes, financing, and logistics. It grew to encompass the State Street, Dearborn-Milwaukee, and West Side Subways, with the latter modernizing the old Garfield Park “L” into the median of Chicago’s first expressway. Take a trip underground and see how Chicago’s “I Will” spirit overcame challenges and persevered to help with the successful building of the subways that move millions. Building Chicago’s subways was national news and a matter of considerable civic pride–making it a “Second City” no more!
Bibliographic information:
Title Building Chicago’s Subways
Images of America
Author David Sadowski
Edition illustrated
Publisher Arcadia Publishing (SC), 2018
ISBN 1467129380, 9781467129381
Length 128 pages
Chapter Titles:
01. The River Tunnels
02. The Freight Tunnels
03. Make No Little Plans
04. The State Street Subway
05. The Dearborn-Milwaukee Subway
06. Displaced
07. Death of an Interurban
08. The Last Street Railway
09. Subways and Superhighways
10. Subways Since 1960
Building Chicago’s Subways is in stock and now available for immediate shipment. Order your copy today! All copies purchased through The Trolley Dodger will be signed by the author.
The price of $23.99 includes shipping within the United States.
For Shipping to US Addresses:

For Shipping to Canada:

For Shipping Elsewhere:

 Redone tile at the Monroe and Dearborn CTA Blue Line subway station, showing how an original sign was incorporated into a newer design, May 25, 2018. (David Sadowski Photo)
Redone tile at the Monroe and Dearborn CTA Blue Line subway station, showing how an original sign was incorporated into a newer design, May 25, 2018. (David Sadowski Photo)
Help Support The Trolley Dodger

This is our 255th post, and we are gradually creating a body of work and an online resource for the benefit of all railfans, everywhere. To date, we have received over 664,000 page views, for which we are very grateful.
You can help us continue our original transit research by checking out the fine products in our Online Store.
As we have said before, “If you buy here, we will be here.”
We thank you for your support.
DONATIONS
In order to continue giving you the kinds of historic railroad images that you have come to expect from The Trolley Dodger, we need your help and support. It costs money to maintain this website, and to do the sort of historic research that is our specialty.
Your financial contributions help make this web site better, and are greatly appreciated.

















































































































































































































![Santa Teresa Tram Rio de Janeiro Original 1974 35mm Kodachrome Slide Subject: CTCG 7 Location: Carioca (R10) Date: March 17, 1974 Photographer: James J. Buckley From the Wikipedia: The Santa Teresa Tram, or Tramway (Portuguese: Bonde de Santa Teresa, IPA: [bõˈdʒi dʒi ˈsɐ̃tɐ teˈɾezɐ]), is a historic tram line in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It connects the city centre with the primarily residential, inner-city neighbourhood of Santa Teresa, in the hills immediately southwest of downtown. It is mainly maintained as a tourist attraction and is nowadays considered a heritage tramway system, having been designated a national historic monument in 1985. The line has a very unusual gauge: 1,100 mm (3 ft 7+5⁄16 in). The main line is 6.0 kilometres (3.7 miles) long. Having run continuously since its opening in 1877 (except for a 2011–15 suspension), it is one of the oldest street railway lines in the world and having been electrically powered since 1896, it is the oldest electric railway in all of Latin America. For many years it was also the only remaining metropolitan tram system in Brazil. The only other original tram systems in the country to have survived past 1971 are the Campos do Jordão interurban tram/light rail line, which continues to operate today, and the Itatinga line (near Bertioga), a rural and non-public tram line which had ceased operation as a tramway by 2017. All other cities closed their systems by 1971 (Santos being the last), but since that time, three towns, Belém, Campinas and Santos, have reinstated trams as heritage services. Rio de Janeiro opened a modern light rail/tram system in 2016. Link to eBay Listing](https://i0.wp.com/thetrolleydodger.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/eba023.jpg?resize=665%2C443&ssl=1)














![Santa Teresa Tram Rio de Janeiro Original 1974 35mm Kodachrome Slide Subject: CTCG 17 Location: Carioca (R10) Date: March 17, 1974 Photographer: James J. Buckley From the Wikipedia: The Santa Teresa Tram, or Tramway (Portuguese: Bonde de Santa Teresa, IPA: [bõˈdʒi dʒi ˈsɐ̃tɐ teˈɾezɐ]), is a historic tram line in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It connects the city centre with the primarily residential, inner-city neighbourhood of Santa Teresa, in the hills immediately southwest of downtown. It is mainly maintained as a tourist attraction and is nowadays considered a heritage tramway system, having been designated a national historic monument in 1985. The line has a very unusual gauge: 1,100 mm (3 ft 7+5⁄16 in). The main line is 6.0 kilometres (3.7 miles) long. Having run continuously since its opening in 1877 (except for a 2011–15 suspension), it is one of the oldest street railway lines in the world and having been electrically powered since 1896, it is the oldest electric railway in all of Latin America. For many years it was also the only remaining metropolitan tram system in Brazil. The only other original tram systems in the country to have survived past 1971 are the Campos do Jordão interurban tram/light rail line, which continues to operate today, and the Itatinga line (near Bertioga), a rural and non-public tram line which had ceased operation as a tramway by 2017. All other cities closed their systems by 1971 (Santos being the last), but since that time, three towns, Belém, Campinas and Santos, have reinstated trams as heritage services. Rio de Janeiro opened a modern light rail/tram system in 2016. Link to eBay Listing](https://i0.wp.com/thetrolleydodger.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/eba008.jpg?resize=665%2C444&ssl=1)